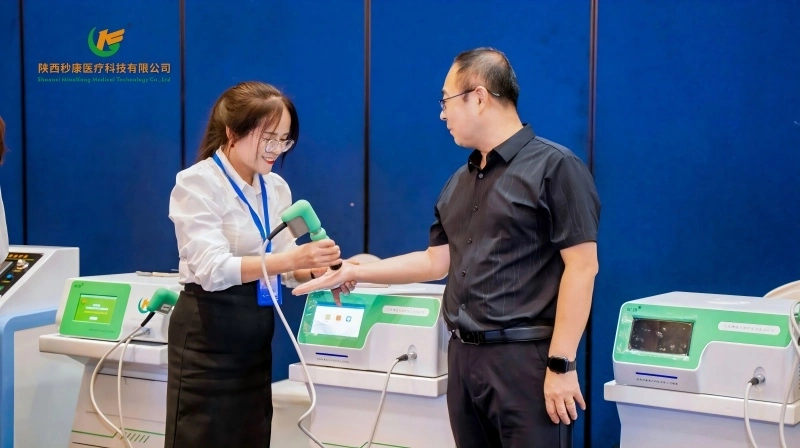
To put it simply, Radial Pressure Wave Therapy (RPWT)—often referred to as pneumatic ballistic therapy—is a specific subset of Shockwave Therapy. They share a "part-to-whole" relationship rather than being identical.
To understand this connection, we can break it down into three dimensions: the core definition of shockwaves, the pneumatic technical principle, and the broader classification of the technology.
1. The Core Definition: What is Shockwave Therapy?
Shockwave therapy refers to a category of medical devices that utilize "shockwaves"—high-energy mechanical pressure waves characterized by a rapid rise in pressure—to treat the musculoskeletal system.
Mechanism: It works by activating local metabolism, improving blood circulation, alleviating pain, and stimulating tissue repair.
Common Applications: Plantar fasciitis, tennis elbow, Achilles tendinopathy, and non-union of fractures.
Key Takeaway: "Shockwave therapy" is the umbrella term for the treatment modality, while "Pneumatic Ballistic" is one specific method used to generate that energy.
2. Pneumatic Ballistic Technology: How it Works
The Pneumatic Ballistic (Radial) device generates what is technically known as a Pressure Wave through an indirect process:
The Process: Compressed air drives a metal projectile (bullet) inside the handpiece at high speed. This projectile strikes an applicator (transmitter) at the end of the device.
The Conversion: The kinetic energy from the impact is converted into a pressure wave, which is then transmitted through the skin into the underlying tissue.
Characteristics: These waves are "radial," meaning they spread out as they go deeper. They are generally gentler than focused waves and are ideal for treating superficial or medium-depth soft tissue and bony pathologies.
3. Comparison of Technical Types (The "Inclusion" Relationship)
To see why they are not identical, we must look at the other technologies that also fall under the "Shockwave Therapy" umbrella:
| Technology Type | Core Principle | Characteristics & Applications |
| Pneumatic Ballistic (Radial) | Compressed air drives a projectile to strike a transmitter. | Gentle energy, flexible operation; ideal for superficial/mid-layer tissue pain. |
| Electromagnetic (Focused) | Electric current passes through a coil to create a magnetic field, vibrating a diaphragm. | Stable energy, precise focal point; ideal for deep-seated tissue and bone issues. |
| Electrohydraulic (Focused) | High-voltage discharge in water creates a spark and a bubble, generating a wave. | High energy; historically used for lithotripsy (breaking kidney stones). |
Summary
Conclusion: A Pneumatic Ballistic Extracorporeal Pressure Wave device is a specific type of Shockwave Therapy. It is a branch of the technology that utilizes air pressure to drive a projectile.
Key Distinction: One cannot say they are "entirely synonymous" because Shockwave Therapy is the broad category. However, in clinical practice, they share the same therapeutic logic: using mechanical waves to trigger a biological healing response in the body.